A fatty dystrophia of liver
Overview
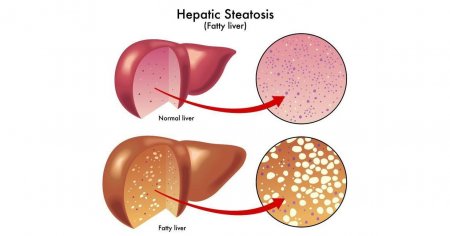
Fats from food are broken down in the gut by enzymes and absorbed into the bloodstream. From there they get to the liver, where they are converted into triglycerides, cholesterol, phospholipids and other necessary substances for our body. Fatty liver accumulation occurs in the case of a high amount of hepatic triglycerides. When fatty degeneration of triglycerides can reach more than 50% of its mass (no more than 5% of normal). Factors leading to this condition varied: high intake of fatty acids with food, increased production of triglycerides in the liver, disturbance of transport triglycerides from the liver to adipose tissue where normal triglycerides are stored in the form of fat. Depending on the nature of the fat deposition fatty liver is divided into the coarse and atomized (the size of fat droplets in the liver cells).
Causes of disease
1.Alcohol abuse is the most common cause of fatty liver. Ethyl alcohol and its metabolism products affect all stages of exchanges of fat in the liver. The severity of steatosis is directly proportional to the amount of alcohol consumed.
2.Diabetes.
3.Obesity and high dietary fat intake.
4.Protein deficiency, Kwashiorkor syndrome (accumulation of fat in the liver due to the insufficient amount of protein and a violation of transport fats from the liver to the tissues).
5.Poisoning hepatotropic poisons (carbon tetrachloride, DDT, yellow phosphorus, etc.).
6.The use of certain medications.
Symptoms
Patients with FH complaints usually do not show. illness flow blurred, slowly progressive. Since there are constant dull pain in the right upper quadrant, can be nausea, vomiting, abnormal stools.
Very rarely observed fatty liver disease with severe clinical picture: severe abdominal pain, jaundice, weight loss, itchy skin.
Diagnostics
Suspected steatosis doctor therapist may have a clinical examination by an increase in the size of the liver during abdominal palpation. Increased liver confirmed by abdominal ultrasound. In the biochemical analysis of blood showed increased liver enzymes (AST, ALT, alkaline phosphatase). In some cases, for confirmation of the diagnosis carried out CT scans, MRI, liver biopsy.
Treatment
Tactics of treatment depends on the cause of the disease. Proper diet, abstinence from alcohol, correction of metabolic disturbances, as a rule, lead to improvement. Assign a diet with a high content of protein, reduced fat, especially animal. Fatty liver associated with alcohol with continued alcohol consumption over time only progresses.