What Is a Lipoma? Symptoms, Causes + 4 Natural Remedies
Do you currently have a lump on your body that feels doughy and moves easily when you touch it? If your answer is “yes,” then you may already be familiar with lipomas. They are actually pretty common with approximately 1 in 100 people experiencing a lipoma at some point in their lives. Most of the time, you have one lipoma at a time, but about 20 percent of people will have several at once.
Can a lipoma become cancer? Typically, this does not occur, but it is important to monitor lipoma for growth and other changes. Is a lipoma painful? It can be. Most of the time, a lipoma won’t cause you pain, but it can hurt if it bumps up against nerves close by or if it has blood vessels running through it.
Is lipoma removal necessary? Many times, it’s not and there are some natural lipoma remedies that may help!
What Is a Lipoma?
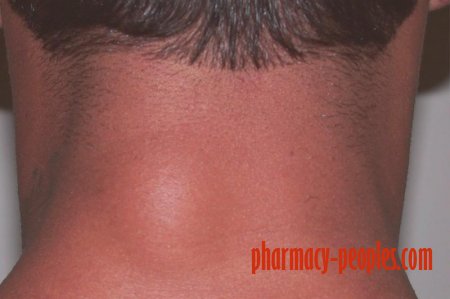
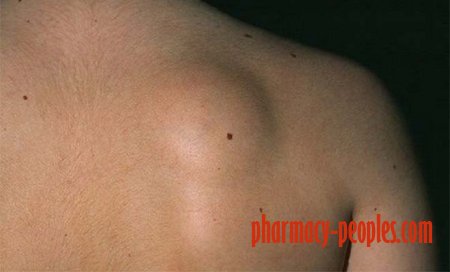
A lipoma is a benign lump that forms under the skin due to an overgrowth of fat cells. A lipoma can occur anywhere on the body where there are fat cells. Lipomas are soft and rounded or lobulated and they easily move around. Most of the time, these lumps are relatively small, but researchers have observed “giant lipomas” that are are larger than the typical maximum of two inches across. (2, 3)
Lipomas most often occur on the neck, trunk and extremities but they can occur anywhere on the body. Can a lipoma become cancerous? A lipoma is considered to be a benign, non-cancerous growth. There is a very rare type of cancer known as liposarcoma, which occurs within fatty tissue and may look like a deep lipoma.
Therefore, lipomas are not cancer, and it’s very rare for a lipoma to turn into a cancerous sarcoma. However, since it’s possible, if you notice that a lipoma starts to change (especially if it grows quickly or becomes painful), alert your doctor who may want to perform a biopsy. (4)
While all lipomas are made up of fat, there are sub-types based on the way they appear under the microscope. Types of lipoma include: (5)
- Conventional lipoma (common, mature white fat)
- Hibernoma (brown fat instead of the usual white fat)
- Fibrolipoma (fat plus fibrous tissue)
- Angiolipoma (fat plus a large amount of blood vessels)
- Myelolipoma (fat plus tissue that makes blood cells)
- Spindle cell lipoma (fat with cells that look like rods)
- Pleomorphic lipoma (fat with cells of all different shapes and sizes)
- Atypical lipoma (deeper fat with a larger number of cells)
Lipoma Signs & Symptoms
Lipomas can occur anywhere in the body. They most often appear in the neck, shoulders, back, abdomen, arms and thighs. It’s less common but possible for lipomas to form in internal organs, bones or muscles.
Lipoma symptoms include a lump that is:
- situated just under the skin
- soft and doughy to the touch
- moves easily with just slight finger pressure
- small (most lipomas are under 2 inches (5 centimeters) in diameter, but they can grow)
- sometimes painful (if they grow and press on nearby nerves or if they contain many blood vessels)
Lipoma Causes & Risk Factors
First of all, lipomas are more common among women. But why do lipomas form?
To date, the cause of lipomas is not completely understood by the medical community. Lipomas often appear after an injury, but doctors aren’t sure whether that’s what makes them form or not.
Risk factors for developing a lipoma include:
- Being between the ages of 40 and 60 years old
- Genetics since lipomas tend to run in families
While lipomas are most common in the 40 to 60 age group, they can certainly occur at any age. Some scientific research points out that single lipomas are seen in predominately in middle-aged women while multiple lipomas are seen more often in men.
Lipoma Diagnosis & Conventional Treatment
It’s usually not hard for doctors to diagnose a lipoma with a basic physical exam. They will inspect the lump and touch the lump to see how it feels. If the lipoma is large and/or painful then your doctor request testing to rule out the possibility of liposarcoma, a rare form of cancer. Possible tests that may be ordered include a biopsy, an ultrasound scan, a CT scan and/or a MRI scan.
It’s very common to have a lipoma, but lipoma removal is often considered unnecessary by your doctor. Rather than remove it, your doctor is likely suggest keeping an eye on the lump and if any changes are noticed, then the situation can be reevaluated by him or her.
In some cases, lipoma removal via lipoma surgery may be determined to be the right course of action by patients themselves. They may be concerned about where the lipoma is located or they may simply not like the appearance of the lump on their bodies.
Elective lipoma surgery may not be covered by your health insurance provider. However, in some situations, your doctor may decide lipoma removal is necessary when it affects muscle development or it causes you pain.
Lipoma treatments to remove the lump can typically be performed using local anesthesia, and you can return home that day. Since, lipomas do not tend to grow into surrounding tissues, they can often be cleanly removed by making a small incision. Once an incision is made, the lipoma is either physically squeezed out or a suction technique to remove fat called liposuction is used to remove the lipoma.
According to the Cleveland Clinic,
The outlook for people with lipomas is extremely positive. Because lipomas are generally harmless and cause no discomfort, they do not affect a person’s quality of life. Lipomas do not increase the risk of other diseases, and people who choose to have their lipomas removed for cosmetic reasons usually have limited scarring.
Since lipoma removal is often unnecessary, let’s now talk about some natural remedies that may help with this relatively common health concern.
4 Lipoma Natural Remedies
Unfortunately, natural remedies for lipoma removal have not been well studied to date. But there are some things you can do that may help to improve a lipoma or avoid one in the first place.
1. Avoid and Reduce Obesity
Scientific research points out that there is a “statistically significant association” between obesity and lipoma development. It’s also been observed that lipomas often occur with the onset of obesity in people of middle age.
Starting at an early age, there are so many natural things you can do to reduce childhood obesity as well as obesity in adulthood:
- Cook more meals at home and focus on consuming a healthy diet rich in healing whole foods, especially high-fiber foods and clean, lean protein like wild-caught fish.
- Cut back on your sugar intake, which is known to directly contribute to the development of chronic diseases, including obesity, heart disease and diabetes.
- Limit sedentary time, such as watching TV, which Harvard research linked with obesity over 25 years ago!
- Exercise! Of course, this is the complete opposite of sitting around. The World Health Organization recommends at least one hour per day of physical activity for children and at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity throughout the week or do at least 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity throughout the week or an equivalent combination of moderate- and vigorous-intensity activity.
2. Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar contains acetic acid and research conducted with obese rats and mice suggest that acetic acid can prevent fat deposition in the body and improve their metabolism. If you’re trying to improve a lipoma, consuming my Secret Detox Drink daily is a great way to get a daily dose of apple cider vinegar plus other well-known healthy ingredients like ginger and raw honey.
3. Avoid Unhealthy Fats
Since lipomas are an accumulation of fatty tissue, I strongly recommend avoiding unhealthy fats in your diet, specifically trans fats. Many people are consuming trans fatty acids daily and don’t even realize it. These health-sabotaging fats are commonly found in fast and processed foods.
Most trans fats in our diets are in the form of artificial trans fats, which are created by adding hydrogen to liquid vegetable oils to make them more solid. These genetically modified cooking oils are not healthy, and they can even become rancid oils that cause even more health problems.
Research has shown that a trans fats diet induces abdominal obesity and changes in insulin sensitivity in monkeys even when an excess of calories were not consumed. These effects are likely the same in humans.
4. Eat More Omega 3-Rich Foods
Instead of unhealthy fats, make sure you include healthy fats in your diet, especially omega-3 fatty acids which are known for their health boosting, anti-inflammatory effects. Research shows that at “sufficiently high intakes,” omega-3 fatty acids, like those found in oily fish and fish oil, actually reduce the production of inflammatory eicosanoids, cytokines and reactive oxygen species, and the expression of adhesion molecules.
Great sources of omega-3 fatty acids include:
- Wild-caught salmon
- Sardines
- Walnuts
- Flaxseeds
- Chia seeds
- Hemp seeds
Precautions
If you see an unexplained lump or swelling on your body, it’s always a good idea to have a doctor take a look at it, especially if it doesn’t go away quickly.
A painful lipoma or a lipoma that grows larger warrants a call and visit to your doctor right away. It is very rare, but it is possible for a lump on the body to be liposarcoma, which is a type of cancerous lump that continues to grow and is painful. Lipomas and liposarcomas can be confused for each other. Liposcarcomas mostly occur in the muscles of the limbs or in the abdomen, but they can be in other locations.
You can always insist on a biopsy to ensure a correct diagnosis of your lipoma.
- Health / Disease
- 14-09-2018, 22:43
- 2 668
- Pharmatic