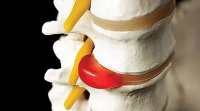
Intervertebral hernia - a protrusion of the inner nucleus pulposus outside the anatomical localization. The core consists of a vertebra cartilage tissue rich in hyaluronic acid content, which gives it a gelatinous but firm texture. On the circumference of the vertebral body nucleus pulposus protected fibrous ring consisting also of cartilage, but of dense collagen fibers. The structure of the intervertebral discs of the spine ensures smooth movements.
Hernia, in fact, is the protrusion of an internal organ or a part thereof beyond the anatomical localization. In the formation of this pathology crucial role played by two factors:
Increased internal pressure;
The destruction of the barrier, fence off internal organs.
At long current inflammatory process occurring degenerative changes in the fibrous ring. The distance between the fibers increases, cracks appear. However, pain in the spine hernias do not appear on that destroyed cartilage, and by compression of the nerve and vascular bundles prolapsed spinal nucleus pulposus tissue, soft and elastic structure is outside the anatomical localization undergoes ossification - ossification. The resulting bone ridges compress the nerves and small blood vessels.